Principle and Application of Digital Temperature Sensor DS1722
Acme Threaded Rod,Screw Rod,Hardware Series Shandong Shanglong Economic and Trade Corporation Ltd , http://www.chthreadedrod.com
I. INTRODUCTION With the continuous advancement and development of science and technology, the types of temperature sensors are increasingly numerous and widely used, and they have begun to develop from analog to digital, single-bus, dual-bus, and three-bus models. The digital temperature sensor is widely used because of the advantages of an automatic temperature control system that is suitable for various microprocessor interfaces and that can overcome the drawbacks of signal conditioning circuits and A/D converters when analog sensors and microprocessors are interfacing. Industrial control, electronic thermometers, medical instruments and other temperature control systems. Among them, the representative digital temperature sensors include DS1820, MAX6575, DS1722, and MAX6635. This article mainly introduces the characteristic of digital temperature sensor DS1722, the method of use and its timing, and describes the temperature measurement system composed of sensor DS1722 and single chip microcomputer 89C51. 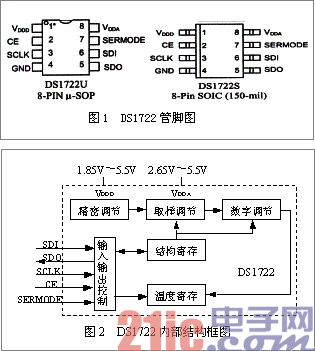
Second, DS1722's working principle 1, DS1722's main features DS1722 is a low-cost, low-power three-bus digital temperature sensor, its main features are shown in Table 1.
2. Internal Structure of DS1722 The digital temperature sensor DS1722 is available in 8-pin m-SOP and 8-pin SOIC packages. The pinouts are shown in Figure 1. It consists of four main components: precision temperature sensors, analog-to-digital converters, SPI/three-wire interface electronics, and data registers. The internal structure is shown in Figure 2. 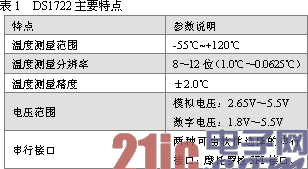
When the power supply is started, the DS1722 is in an energy-off state. After power is supplied, the user can make it in continuous conversion temperature mode or single conversion mode by changing the register resolution. In the continuous conversion mode, the DS1722 continuously converts the temperature and stores the result in the temperature register. Reading the temperature register does not affect the temperature conversion. In the single conversion mode, the DS1722 performs a temperature conversion and the result is stored in the temperature register. Back to off mode, this conversion mode is suitable for temperature-sensitive applications. In the application, the user can set the resolution register by program to achieve different temperature resolutions. There are five resolutions in 8-, 9-, 10-, 11-, or 12-bit resolution, and the corresponding temperature resolution is 1.0°C. 0.5 °C, 0.25 °C, 0.125 °C or 0.0625 °C, the default resolution for temperature conversion results is 9 digits. The DS1722 has two communication interfaces, a Motorola serial interface and a standard three-wire interface. Users can select the communication standard through the SERMODE pin.
3, DS1722 temperature operation method The sensor DS1722 converts the temperature into a digital quantity and stores it in the temperature register in the binary complement format. Through SPI or a three-wire interface, the data in addresses 01H and 02H in the temperature register can be read out. The address of the output data is shown in Table 2. The exact relationship between the binary format of the output data and the hexadecimal form is shown in Table 3. In Table 3, assume that the DS1722 is configured for 12-bit resolution. The data is transmitted continuously through the digital interface, the MSB (most significant bit) is transmitted first through the SPI, and the LSB (least significant bit) is first transmitted over the three wires. 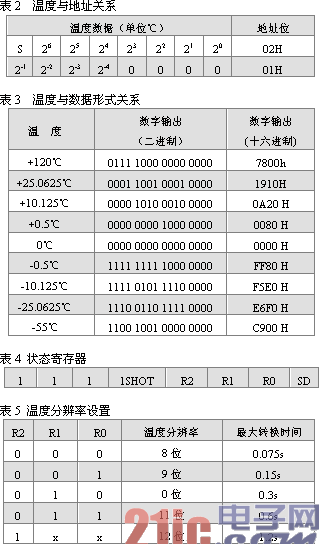
4. The working procedure of DS1722 DS1722 All working procedures are completed by SPI interface or three bus communication interface by selecting the appropriate address of the status register. Table 4 shows the register address table, which shows the addresses of the DS1722's two registers (state and temperature).
1SHOT is a single-step temperature conversion bit and SD is a shutdown bit. If the SD bit is "1", continuous temperature conversion is not performed. When the 1SHOT bit is written to "1", the DS1722 performs a temperature conversion and stores the result in address bits 01h (LSB) and 02h (MSB) of the temperature register. 1SHOT automatically clears “0†after temperature conversion. If the SD bit is "0", the continuous conversion mode is entered and the DS1722 continuously performs the temperature conversion and stores all the results in the temperature register. Although the data written to the 1SHOT bit is ignored, the user still has read/write access to this bit. If you change SD to "1", the ongoing conversion will continue until it is complete and the result is stored, and the device will then enter the low power off mode.
The default 1SHOT bit is "0" when the sensor is powered on. R0, R1, R2 are the temperature resolution bits, as shown in Table 5 (x = any value). The user can read and write access to R2, R1, and R0 bits. When powered on, R2 = "0", R1 = "0", and R0 = "1" (9-bit conversion). At this point, the communication port remains valid, the user has read/write access to the SD bit, and its default value is "1" (off mode).
Third, DS1722 temperature measurement system design 1, software design Sensor DS1722 provides two kinds of serial interface modes, when the mode strobe SERMODE connected to VDDD selects SPI communication, when the pin is grounded, select the standard three bus communication. 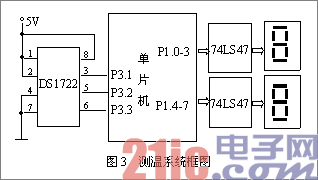
Taking the three-bus mode as an example, the hardware circuit of the temperature measurement system is composed of a digital temperature sensor DS1722, a single-chip AT89C51 and a display part. Use P1 mouth to make the data output port, the temperature signal collected is sent to P1 mouth after being dealt with by the one-chip computer, send to the seven-segment code decoder display through 74LS47 drive. Its circuit block diagram is shown as in Fig. 3.
2. The design of the software design software is divided into four major parts: the data acquisition part, the data part integer conversion part, the data fraction part conversion part, and the data display part. The system software flow is shown in Figure 4. 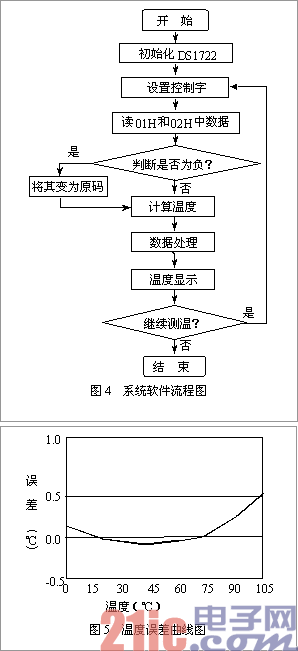
4. Temperature measurement results and analysis In the process of temperature measurement, the sensor DS1722 is placed in a container mixed with ice and water at 0° C. and the container is gradually heated up. The water temperature in the container is observed with a thermometer, and the sensor is processed after processing by the single chip microcomputer 89C51. The output temperature value, the resulting data shown in Table 6. If the formula "absolute error = actual temperature - measured temperature" is used to calculate the error of the temperature sensor DS1722, the experimental data shows that as the temperature increases, the experimental error becomes larger and larger. The error vs. temperature curve is shown in Figure 5.
As can be seen from Figure 5, the temperature error of the sensor DS1722 is linearly related to the temperature, and the factors that produce the temperature error are approximately the following:
(1) The factors of the experimental circuit itself;
(2) Human factors, there may be human error in readings;
(3) Environmental factors, because the sensor is placed in the tube, there is a certain difference between the tube temperature and the water temperature;
(4) The sensor itself, the sensor is welded to the eight-legged double-inline tube holder during the experiment, and can not fully contact with the tube wall, which also has certain errors.
Considering the above factors comprehensively, this error range is allowed by the sensor DS1722, so the experimental data is real and effective.
V. Conclusion The digital temperature sensor DS1722 can accept wide-range analog signals and low-power digital logic signals, thus meeting the growing demand for multiple voltages in portable and mixed-signal systems. The addition of standard three-wire and SPI serial interfaces allows designers great flexibility in using different network communication protocols in embedded systems.
The application field of the digital temperature sensor DS1722 may involve personal computers/servers/workgroups, cell phones, office equipment, or any heat-sensitive system. The disadvantage is that it cannot be exposed to the environmental pressures required by some industrial applications, such as combustion. It is believed that with the increase of DS1722 users, it will surely play a greater role.
